CCF evaluation for redundant architectures
CCFs (Common Cause Failures) are failures due to a single cause that can affect multiple components at the same time.
CCFs can occur simultaneously on multiple components due to a shock, or due to an increase in system stress (e.g increase in temperature, humidity, vibration), or due to electromagnetic interference, or due to design errors.
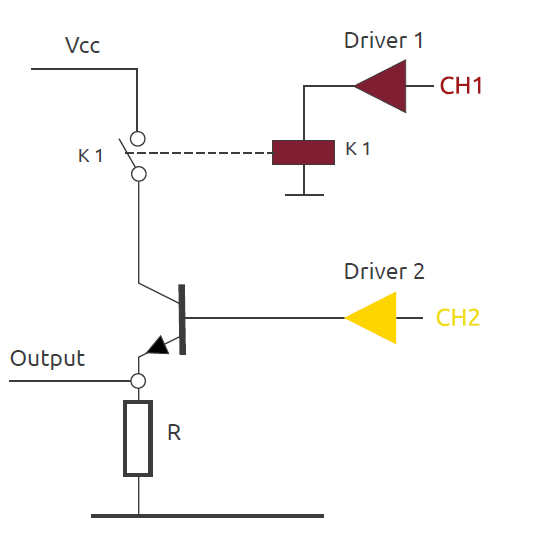
It is important to consider whether common cause failures can occur. These failures can nullify the effects of redundancy. Indeed, if two or more distinct channels in a multichannel system are simultaneously in a faulty state because of common cause failures, the entire safety-related control system could lose the protective effect.
For Cat. 2, Cat. 3 and Cat. 4 it is therefore necessary to implement defence strategies in order to reduce the probability of having CCF. Reduction of the coupling factor between two indipendent channels, choice of robust components, increase of the inherent reliability of the system and keeping the operating environment within the design constraints are some of the defence strategies.
ISO 13849-1 presents a list of 10 measures in Table F.1.
The measures are grouped into the following categories:
Physical design | Separation / segregation Diversity / redundancy Complexity / design / application / maturity / experience |
| Analysis | Data evaluation / analysis and feedback |
| Human problems | Expertise / training / safety culture of designers |
| Environment problems | EMC / Environmental control / pollution of fluidic systems |
A score is assigned to each of the measure listed in the table. The total sum is 100. A score of 65 or better must be achieved. With a score of 65 it is conceivable that the residual fraction of common cause failures is less than or equal to 2%. If, on the other hand, the total score is less than 65, further measures must be taken.
The highest credits are assigned to measures against environmental influences (25 points) and to the use of different technologies / physical principles for the two channels in a two channel system (20 points).